Students are part of large team that achieved fusion ignition for the first time in a laboratory.
Plasma Science and Fusion Center
For more than half a century, researchers around the world have been engaged in attempts to achieve fusion ignition in a laboratory, a grand challenge of the 21st century. The High-Energy-Density Physics (HEDP) group at MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center has focused on an approach called inertial confinement fusion (ICF), which uses lasers to implode a pellet of fuel in a quest for ignition. This group, including nine former and current MIT students, was crucial to an historic ICF ignition experiment performed in 2021; the results were published on the anniversary of that success.
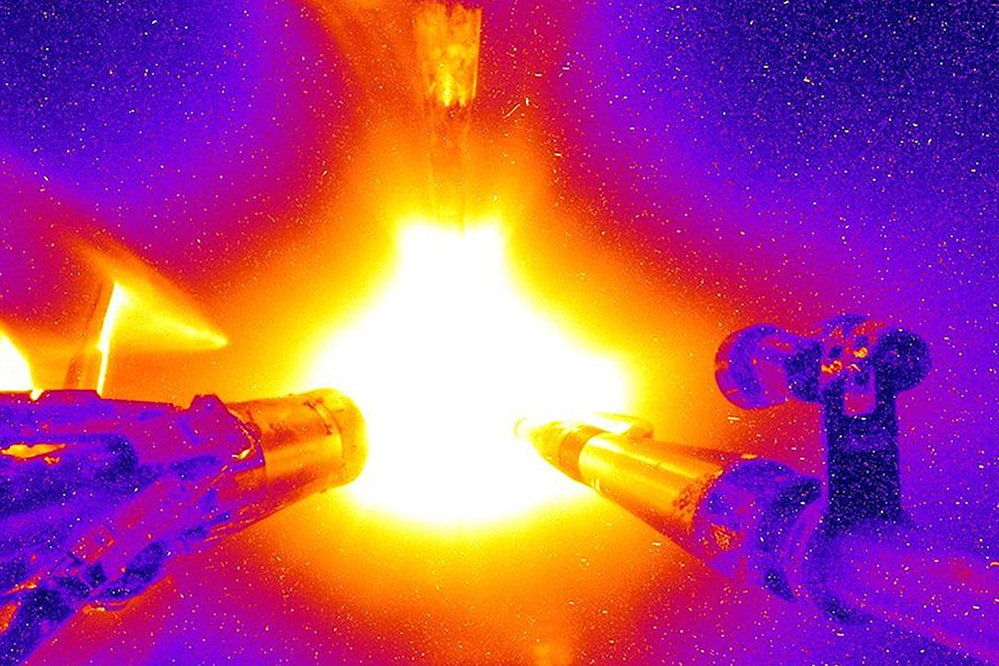
On Aug. 8, 2021, researchers at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), used 192 laser beams to illuminate the inside of a tiny gold cylinder encapsulating a spherical capsule filled with deuterium-tritium fuel in their quest to produce significant fusion energy. Although researchers had followed this process many times before, using different parameters, this time the ensuing implosion produced an historic fusion yield of 1.37 megaJoules, as measured by a suite of neutron diagnostics. These included the MIT-developed and analyzed Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRS). This result was published in Physical Review Letters on Aug. 8, the one-year anniversary of the ground-breaking development, unequivocally indicating that the first controlled fusion experiment reached ignition.
Governed by the Lawson criterion, a plasma ignites when the internal fusion heating power is high enough to overcome the physical processes that cool the fusion plasma, creating a positive thermodynamic feedback loop that very rapidly increases the plasma temperature. In the case of ICF, ignition is a state where the fusion plasma can initiate a “fuel burn propagation” into the surrounding dense and cold fuel, enabling the possibility of high fusion-energy gain.
“This historic result certainly demonstrates that the ignition threshold is a real concept, with well-predicted theoretical calculations, and that a fusion plasma can be ignited in a laboratory” says HEDP Division Head Johan Frenje.
The HEDP division has contributed to the success of the ignition program at the NIF for more than a decade by providing and using a dozen diagnostics, implemented by MIT PhD students and staff, which have been critical for assessing the performance of an implosion. The hundreds of co-authors on the paper attest to the collaborative effort that went into this milestone. MIT’s contributors included the only student co-authors.
“The students are responsible for implementing and using a diagnostic to obtain data important to the ICF program at the NIF, says Frenje. “Being responsible for running a diagnostic at the NIF has allowed them to actively participate in the scientific dialog and thus get directly exposed to cutting-edge science.”
Students involved from the MIT Department of Physics were Neel Kabadi, Graeme Sutcliffe, Tim Johnson, Jacob Pearcy, and Ben Reichelt; students from the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering included Brandon Lahmann, Patrick Adrian, and Justin Kunimune.
In addition, former student Alex Zylstra PhD ’15, now a physicist at LLNL, was the experimental lead of this record implosion experiment.
